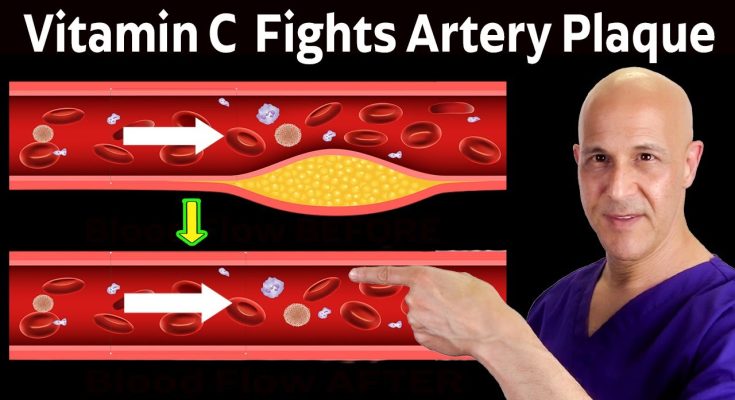
I want to dive into the Intriguing aspect of cardiovascular health specifically challenging the notion that the primary drivers for atherosclerosis or clogging of those arteries are simply cholesterol and dietary fat recent discussions in the field reveal that lipoproteins are the key players in cardiovascular atherosclerosis and these lipoproteins transport cholesterol and triglycerides through the bloodstream and their elevated levels are often associated with an increased risk of heart disease however it’s essential to note that not
all lipo proteins are created equal the composition and function of these particles play a crucial role in how they impact arterial health and an interesting point raised in the interaction between vitamin C and lipoproteins vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that protects the arteries from oxidative stress a significant contributor to the development of atherosclerosis and high dose vitamin C has been suggested to limit harmful effects of lipoproteins by reducing inflammation and potentially reversing the progression of atherosclerosis or
clogged arteries and here’s what’s important most animals synthesize their own vitamin C from glucose allowing them to maintain higher levels of this vital nutrient which explains lower instances of cardiovascular disease in these species lower risk of heart disease clogged arteries in contrast humans lost the ability to produce vitamin C through Evolution necessitating diary sources and many people do not consume enough fruits and vegetables resulting in suboptimal or lower vitamin C levels insufficient intake increases the risk
of developing cardiovascular diseases illustrating the potential link between vitamin C deficiency and heart health so to ensure adequate vitamin C intake it’s beneficial to incorporate a variety of foods rich in nutrients in your diet the best sources of vitamin C are our citrus fruits such as oranges grapefruits and lemons our berries such as our strawberries blueberries raspberries kiwi pineapple papaya bell peppers especially those red ones and yellow ones they have more vitamin C in them as well as our green leafy
vegetables or brussels sprouts or spinach our broccoli even our Tomatoes they are all rich in vitamin C and the research supports the beneficial role of vitamin C in combating atherosclerosis for instance a study published in the Journal of atherosclerosis found that individuals with higher vitamin C levels in their blood had a significantly lower risk of atherosclerosis atherosclerotic plaque buildup in their arteries and another notable study published in the American journal of clinical nutrition indicated
that vitamin C supplementation improved endothelial function and arterial Health in patients with existing cardiovascular disease suggesting that vitamin C May prevent atherosclerosis it can actually help reverse some of its damaging effects as well but there’s one crucial thing we need to be aware of is stress because it depletes vitamin C in the body since this nutrient is used to combat oxidative stress and inflammation and during stressful times the demand of vitamin C increases making it especially important to maintain our adequate
intake levels so chronic stress can contribute to lower vitamin C levels further exacerbating cardiovascular risk factors and the physiological function of vitamin C goes beyond just being an antioxidant it plays a vital role in collagen synthesis which is essential for maintaining the structural Integrity of our blood vessels adequate collagen levels helps keep Our arteries flexible it reduces the likelihood of plaque buildup and furthermore vitamin C is involved in the regulation of nitric oxide a molecule that helps maintain
vasil dilation by opening up the blood vessels promoting a healthier blood flow and this will help improve our blood circulation and reduce high blood pressure as Vitamin C contributes to overall cardiovascular health and various studies highlight the benefits of vitamin C supplementation and individuals who take high doses of vitamin see not only experience improvements in their endothelial function inside the arteries the lining in the arteries but also have lower levels of inflammatory markers associated with heart disease and in
summary the relation a ship between vitamin C lipoproteins and cardiovascular health is an exciting area of research emphasizing a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help ensure adequate intake of vitamin C which can help reduce the risk associated with atherosclerosis or clogging of the arteries and for optimal hard Health a minimum of at least 1,000 Mig of vitamin C per day is recommended and ultimately understanding that the path to heart health encompasses much more than simply managing cholesterol levels opens new
doors for preventing strategies and incorporating high doses of Vitamin C could play a significant role in supporting cardiovascular health and potentially reversing some forms of atherosclerosis by addressing the underlying oxidative stress caused by these lipoproteins and as we continue to explore the intricate connection between nutrition and heart health it becomes clear that a holistic approach is essential in promoting long-term wellness and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and I hope this video serves you well please share
it with your friends and family leave your comments below and most important make it a great day I’m Dr Alan mandal
Here are the key points “Vitamin C and Atherosclerosis (Plaque Buildup in Arteries): What You Should Know! Dr. Mandell”:
- Role of Lipoproteins: Lipoproteins, which transport cholesterol and triglycerides, are crucial in cardiovascular atherosclerosis, challenging the idea that cholesterol and dietary fat are the primary causes.
- Vitamin C’s Impact : Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant, can protect arteries from oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially reversing or limiting atherosclerosis.
- Human vs. Animal Vitamin C Production: Unlike animals, humans can’t synthesize vitamin C, making dietary intake essential to prevent cardiovascular disease due to lower natural levels.
- Vitamin C Sources and Benefits: Rich sources include citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers, and green leafy vegetables. Studies suggest high vitamin C levels and supplementation can improve endothelial function and lower cardiovascular risk.
- Stress and Vitamin C: Stress increases vitamin C demand and depletes levels, which can exacerbate cardiovascular risk. Adequate vitamin C is crucial for maintaining arterial health and overall cardiovascular function.